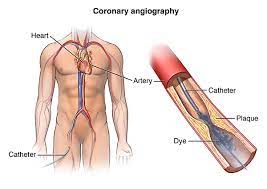
Angiography
Dr Pankaj Patil is a DM cardiologist who routinely conducts angiography. With over 10000 angiographies conducted in the last ten years of practice, he can assist in the routine and emergency detection of cardiac problems. He performs angiographies in various affiliated Kalyan-Dombivli hospitals.
What is Angiography?
Angiography is used to detect blockages in the coronary arteries. The gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery blockage is angiography. During angiography, a contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries using a catheter (thin plastic tube) and the cardiologist observes the blood flow in the heart’s arteries using an X-ray screen. Dr Pankaj Patil is an expert in advanced radial angiography, which is considerably superior to traditional angiography.
Angiography will give the cardiologist:
The precise location and degree of coronary artery obstruction.
Essential for individuals who have suffered a severe heart attack, unexplained heart failure, or unusual chest pain. Based on the results, the cardiologist can plan treatment such as balloon angioplasty, coronary stenting, and coronary artery bypass surgery.
The patient is usually discharged the same day after a successful angiography. If the angiography results indicate blockage/s then appropriate surgery like angioplasty, bypass surgery or balloon plasty maybe done at the same time. It can be a life-saving measure.
How is angiography done?
Coronary angiography is performed with a local anesthesia. The patient is awake all through the procedure.
Dr Pankaj Patil conducts radial angiography, in which a tiny catheter is gently inserted into the artery from the arm (for radial procedure) unlike in conventional procedure where the catheter is inserted via groin. Catheter is pushed into the heart.
X-ray images of the heart and blood vessels are taken after a small amount of contrast dye is injected via catheter.
If the coronary arteries are blocked, appropriate cardiac procedure is done simultaneously
On completion of the surgery, the catheter is removed, and the artery is pressure-sealed to stop the bleeding.
The Radial Approach is superior to the typical procedure in which the catheter is put via the groin. In such circumstances, the patient is unable to move his or her legs for more than 12 hours and must remain in the hospital for an extended period. Radial angiography is convenient and facilitates better angioplasty.

Angioplasty
Having performed thousands of angioplasties in the last ten years of his practice and saving many lives by timely medical intervention, Dr Pankaj Patil is an expert in radial coronary angioplasty. An angioplasty is a life-saving cardiac surgery done to open blocked heart arteries.
Fat, cholesterol, or plaque build-up causes blockage of the coronary arteries. These blockages prevent blood flow to the heart muscles. As a result of a lack of oxygenated blood, the heart muscles begin to die. It’s a heart attack. Alternatively, a block in blood circulation can trigger chest pain and shortness of breath, both of which require treatment to save life.
Angioplasty is inserting a catheter with a small inflatable balloon on the end into an arterial blockage. As a result, it’s often referred to as Balloon Angioplasty. A stent is then inserted to open the obstruction. A cardiologist performs coronary angiography prior to coronary angioplasty.
What are the advantages of Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is a life-saving cardiac surgery for a patient who has suffered a heart attack
It restores blood flow in a relatively short period of time
Angioplasty immediately reduces symptoms such as chest discomfort, tiredness, and shortness of breath.
Cardiologists are now able to conduct angioplasty more efficiently as medical technology progresses.
The doctor recommends the patient to keep a healthy lifestyle following the Angioplasty surgery. Patients must always take their medications exactly as prescribed by their cardiologist. The patient should refrain from smoking and drinking. Regular exercise and a nutritious diet can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
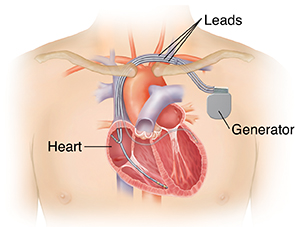
Pacemakers
Pacemakers are small, battery-powered devices used to treat arrhythmias. Arrhythmia is a heart condition in which the heart beats too fast, too slow, or with irregular rhythms. Your cardiologist will implant a pacemaker in your chest to regulate or control abnormal cardiac rhythms or irregular heartbeats. It delivers the heart a signal to beat at a normal rate. There are now several types of pacemakers, including Single chamber/dual chamber, AICD, and CRT-D. To treat arrhythmia in patients, Dr Pankaj Patil offers permanent pacemakers.
A pacemaker is required if the heart beats too slowly. This can lead to exhaustion, fainting, shortness of breath, organ failure, and ultimately death.
Pacemaker controls the electrical system of the body, which regulates heart rhythm.
Pacemaker can monitor and track heartbeat. This record aids the cardiologist in gaining a better insight of arrhythmia.
What happens after the pacemaker is implanted?
Pacemaker surgery typically takes between one and two hours. Patient is discharged after he / she has stabilised, and the pacemaker is working properly. During follow-up appointments, the doctor can also adapt the programme to the patient’s needs.
The patient should take prescribed medications.
The patient should not conduct any strenuous exercises.
Some electric and electronic devices can interfere with the functioning of pacemaker. Hence, you need to avoid use of mobile phones, MP3 players, microwave ovens, High-tension wires, Metal detectors, Welding machines, Electrical generators, etc.

Pediatric Device Closure
Children with heart problems like holes in the heart can now get treatment through a small tube in the groin instead of having major heart surgery.
What are the different kinds of heart problems that babies are born with?
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a type of heart disease in children that is present from birth. The septum is the wall that separates the upper chambers of the heart. In ASD disease, the septum has a hole. ASD happens when the baby’s heart wall doesn’t form right while the mother is pregnant.
In Atrial Septal Defect (ASD), blood flows from the left side of the heart to the right side, mixing oxygenated blood with blood that doesn’t have oxygen. So, the heart sends oxygenated blood back to the lungs instead of the rest of the body.
Why do children get Atrial Septal Defects (ASD)?
During the first eight weeks of pregnancy, the baby’s heart starts to form. As the heart grows, a wall called the septum is made that divides it into two parts. During this process, ASD happens when the dividing doesn’t finish and a hole is left in the atrial septum.
ASD is also caused by genes in a big way. Heart problems can also be caused by gene defects, chromosome abnormalities, and environmental factors.
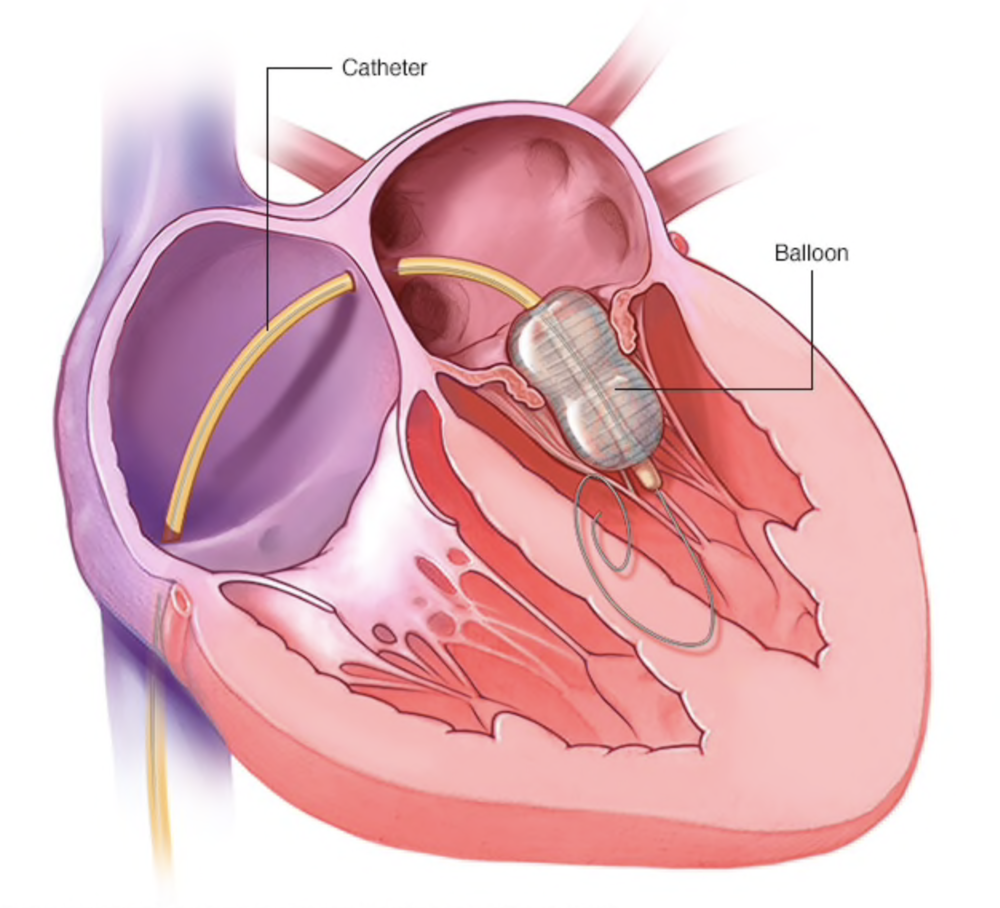
Balloon Mitral Valvuloplasty
Balloon Mitral Valvuloplasty is a type of cardiac surgery done to repair a heart valve with a narrow opening.
To allow blood to pass through the heart, the pulmonary, tricuspid, mitral, and aortic valves all open and close constantly. When a heart valve is narrowed (stenosis), the valve flaps (leaflets) may become thicker, stiffer, and fuse together. Valve stenosis reduces blood flow across the affected valve.
A valvuloplasty can increase the flow of blood through the heart valve. It can also help with problems with the heart valves, like shortness of breath or pain in the chest.
When does the cardiologist recommend Valvuloplasty?
In the following circumstances, a cardiologist will recommend valvuloplasty:
- Patient has a narrow heart valve (valve stenosis)
- Patient’s mitral valve has shrunk in size.
- There is narrowing of the tricuspid valve (tricuspid stenosis)
- There is stenosis of the pulmonary valve (PV) (pulmonic stenosis)
Some varieties of heart valve stenosis, if left untreated, can lead to irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias) or possibly heart failure.
You and your heart doctor can determine whether valvuloplasty or another treatment is suitable for your type and stage of heart valve disease. If a severely constricted valve is generating problems, valvuloplasty may be the appropriate treatment for you. But occasionally, even in the absence of significant symptoms, your cardiologist may prescribe valvuloplasty for heart valve dysfunction.
